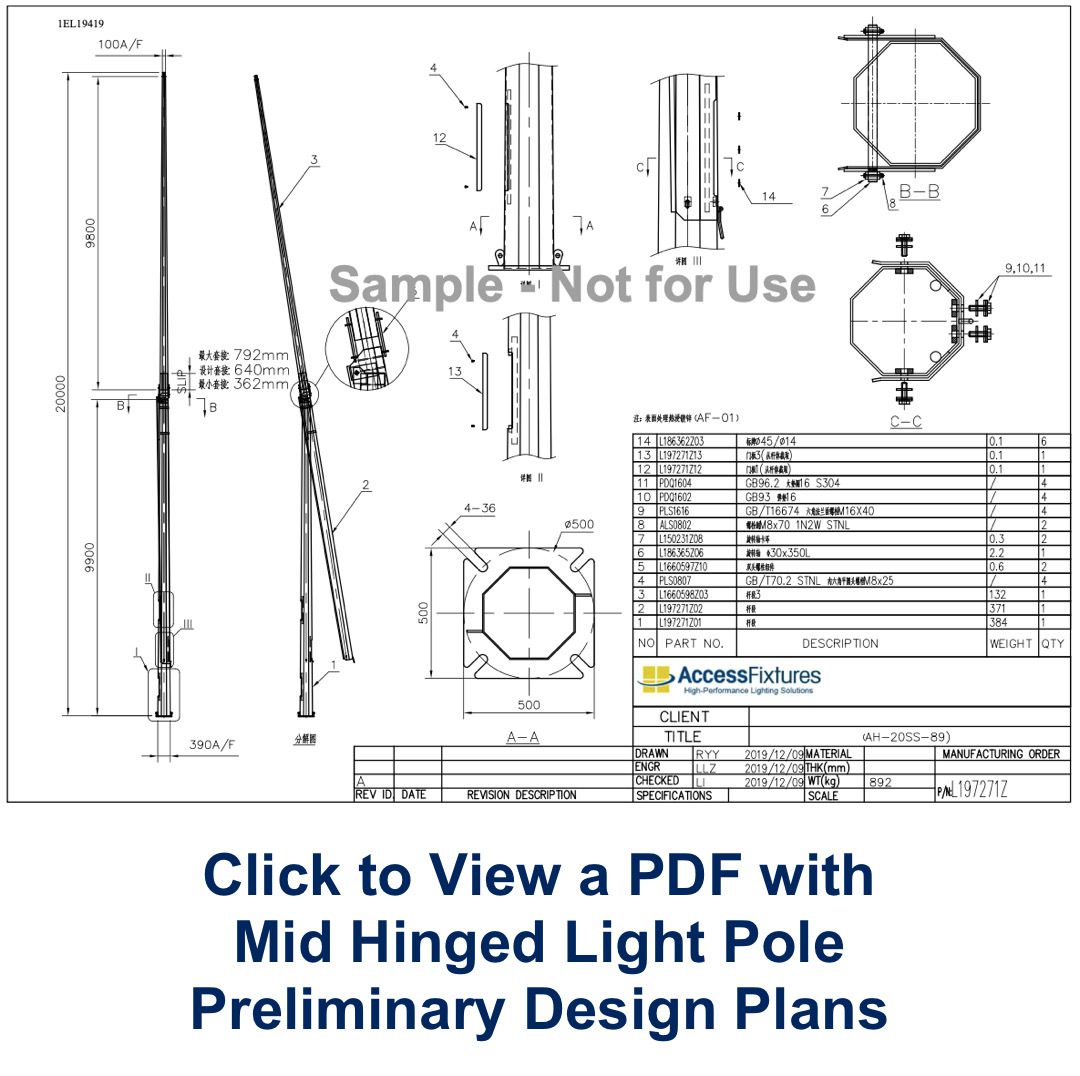
Mid Hinged Light Poles – LED Pole Lighting
Mid-hinged light poles, also known as mid-hinged columns or break-back poles, are specialized types of light poles designed to facilitate maintenance, particularly in places where the use of elevated work platforms or mobile ladders is impractical. These poles are typically constructed with a hinge mechanism located near the midpoint of the pole. This design feature allows the pole to be lowered horizontally to the ground, enabling easy access to the light fixtures and other equipment mounted on the pole.
Key Takeaways
-
-
Ease of Maintenance and Safety: Mid-hinged light poles are specifically designed to reduce the difficulty and risk associated with maintaining high fixtures. By allowing the pole to hinge and lower to ground level, they eliminate the need for climbing or the use of heavy lifting equipment, making routine maintenance and adjustments safer and more accessible to a wider range of personnel.
-
Versatility and Customization: These poles are highly customizable and can be engineered to support a variety of attachments, including lights, cameras, wind turbines, and solar panels. This adaptability makes them suitable for diverse environments and requirements, ranging from urban streets to remote locations like the Arctic.
-
Operational Efficiency: The mid-hinged design simplifies the operation with features like hand winches or motorized systems, allowing a single person to easily raise and lower the pole. This functionality is not only time-efficient but also cost-effective, as it reduces labor costs and the need for additional equipment.
-
5 Reasons to Choose Mid Hinged Poles
Mid-hinged poles offer several practical benefits that make them a preferable choice for various applications, especially in settings where frequent maintenance is required, or where aesthetics and safety are primary concerns. Here are detailed reasons for choosing mid-hinged poles:
1. Ease of Service
The primary advantage of mid-hinged poles is the ease with which they can be serviced. Traditional high mast poles often require specialized equipment or climbing, which can be time-consuming and requires technical expertise. Mid-hinged poles can be lowered to the ground, bringing the top of the pole and any mounted equipment—such as lights, cameras, or sensors—directly to a manageable level. This is particularly beneficial now that lighting technology includes elements like solar panels and wind turbines, which require regular maintenance to ensure they are functioning efficiently.
2. Safety
Safety is a significant concern when servicing equipment at height. Climbing tall poles not only poses a risk of falls but also requires safety gear and training, adding to the operational costs. Mid-hinged poles can be lowered easily by a single person using a manual or motorized system, dramatically reducing the risk of accidents related to working at heights.
3. No Climbing Required
With mid-hinged poles, the necessity to climb is eliminated. This is crucial not just from a safety standpoint but also for practical reasons. Older technicians or those with physical limitations might find climbing particularly challenging. Mid-hinged poles democratize maintenance tasks, allowing a broader range of personnel to perform them without the physical strain associated with climbing.
4. Visual Intrusion Minimization
In scenic areas where the visual impact of infrastructure can be a concern, mid-hinged poles provide an aesthetic solution. They can be lowered when not in use, thereby reducing their visual presence and minimizing their impact on landscapes and views. This feature is particularly valued in historic areas, parks, or residential areas where the community may value unobstructed views of natural or architectural beauty.
5. Versatility and Adaptability
These poles can be adapted to a variety of environments and purposes. They can be used not only for lighting but also for mounting other equipment such as banners, flags, and signs that may need to be lowered or removed at certain times. This versatility makes mid-hinged poles a practical solution for multiple applications, enhancing their utility and cost-effectiveness.
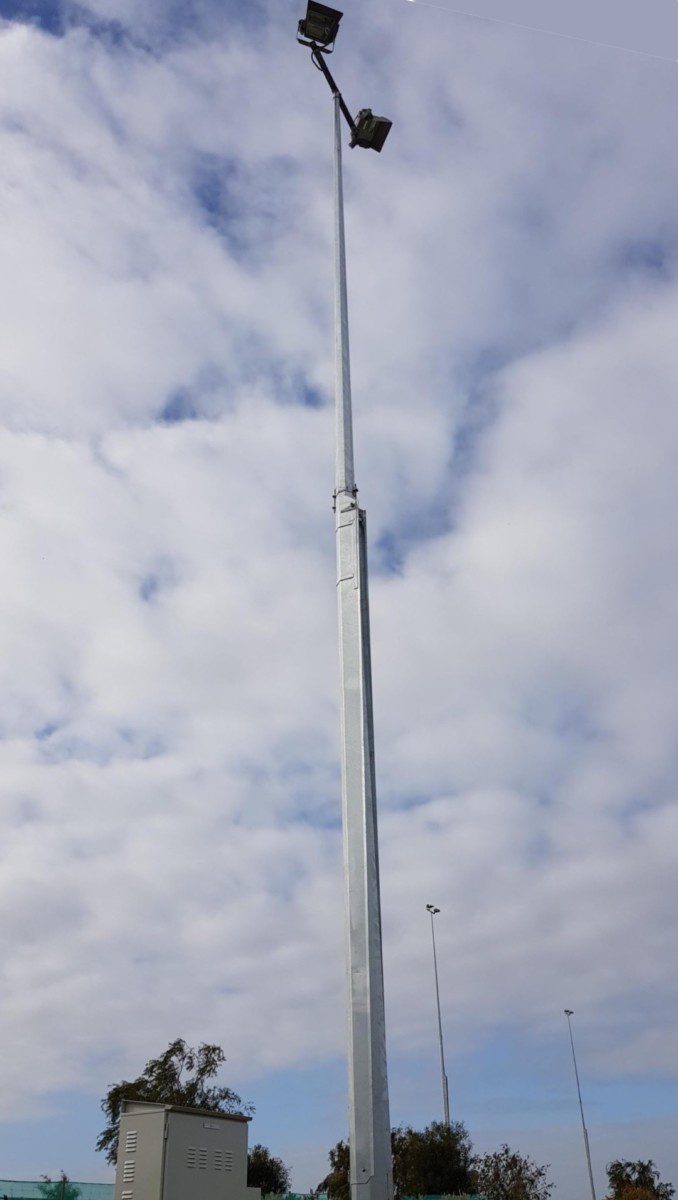

Mid-Hinged Light Pole With 2 Area Lights
Mid Hinged Light Pole Features
Mid-hinged poles are designed to streamline the maintenance and adjustment process, making them a user-friendly option for various settings, from urban areas to remote locations. These poles incorporate several key features to enhance their practicality and ease of use:
- Single Operator Functionality: One of the most significant features of mid-hinged poles is that they can be raised and lowered by a single operator. This design simplifies the process, reducing labor costs and the need for specialized training. The mechanism is straightforward enough that routine adjustments or maintenance can be handled quickly and safely without additional help.
- Quick Adjustment Time: Raising and lowering the pole is highly efficient, typically taking only about one minute. This rapid adjustment capability ensures minimal disruption, whether it’s for routine maintenance, emergency repairs, or reconfiguration of the lighting setup. This quick operation is particularly beneficial in environments where changes in lighting or equipment setups are frequently needed.
- Versatile Raising and Lowering Options: Mid-hinged poles offer various mechanisms to accommodate different environments and operator preferences, including:
- Hand Winch: A manual option that provides a cost-effective and simple solution. It requires no power source, which is ideal for locations without reliable electricity access.
- Motorized Winch: This option is suitable for situations where ease and speed are priorities. It is especially useful for heavier or more complex setups, reducing physical strain and operational time.
- Counterbalance Weight: Some mid-hinged poles use a counterbalance system to simplify the lowering and raising process. This system can help balance the load, making the operation smoother and requiring less manual effort from the operator.
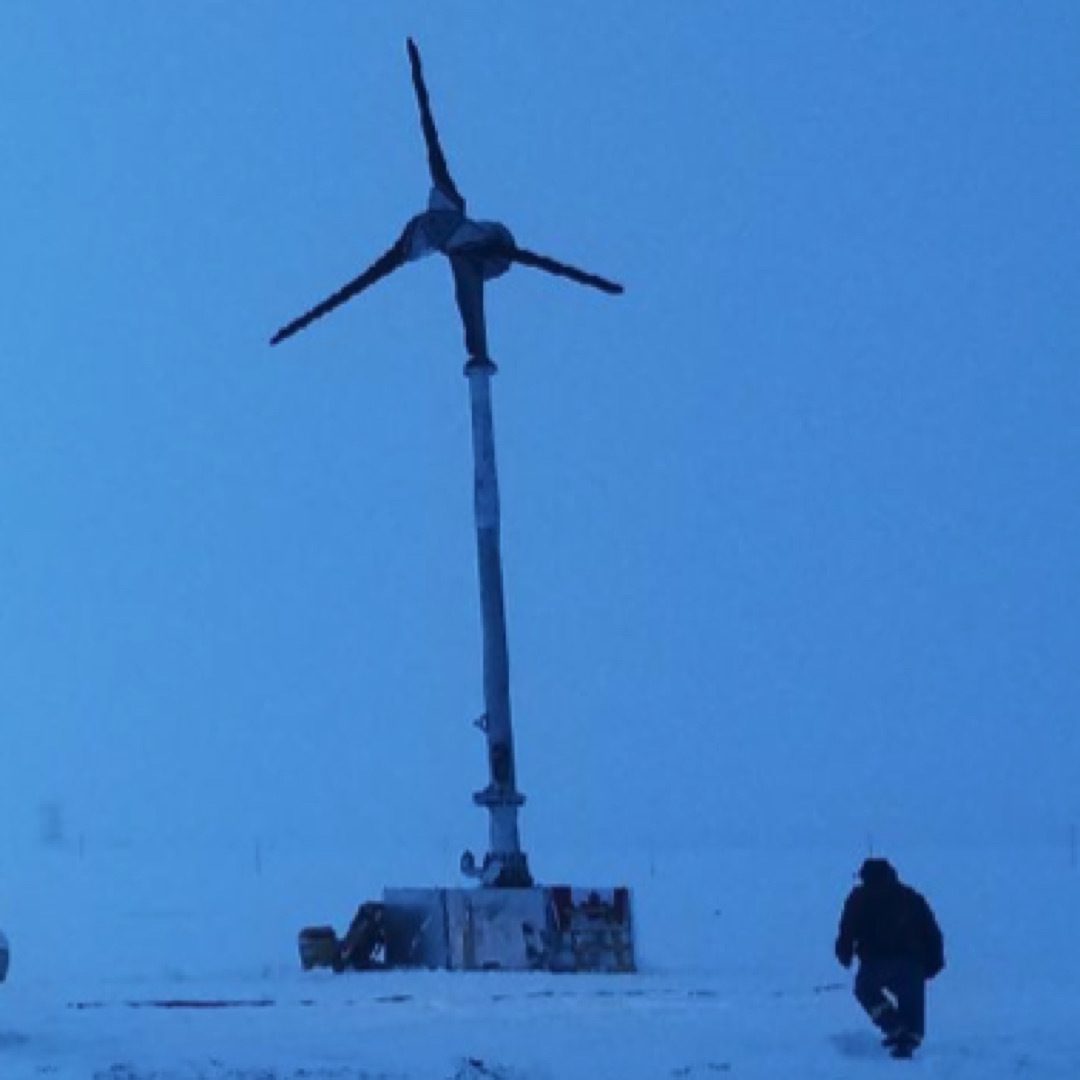
Mid-Hinged Pole for Wind Energy
Discuss your specific job requirements with a lighting specialist. Contact us today.
Mid Hinged Pole Height and Mechanisms
Mid-hinged pole structures are highly customizable, designed to meet specific needs and specifications, which makes them versatile for a variety of applications. Here’s a more detailed look at their design, engineering, and operational features:
Custom Design and Engineering
Mid-hinged poles are engineered to order, which means each pole can be specifically tailored to meet the dimensional and mechanical requirements of its intended use. There is no strict limit to the height or the load capacity of these poles, as long as the design adheres to engineering principles and safety standards. Typically, these poles are designed to stand up to 65 feet, which suits a wide range of applications, from street lighting to specialized industrial uses. The capacity to support equipment, like lights, cameras, wind turbines, or other devices, is determined by the structural calculations to ensure stability and safety.
Mounting Options and Capacity
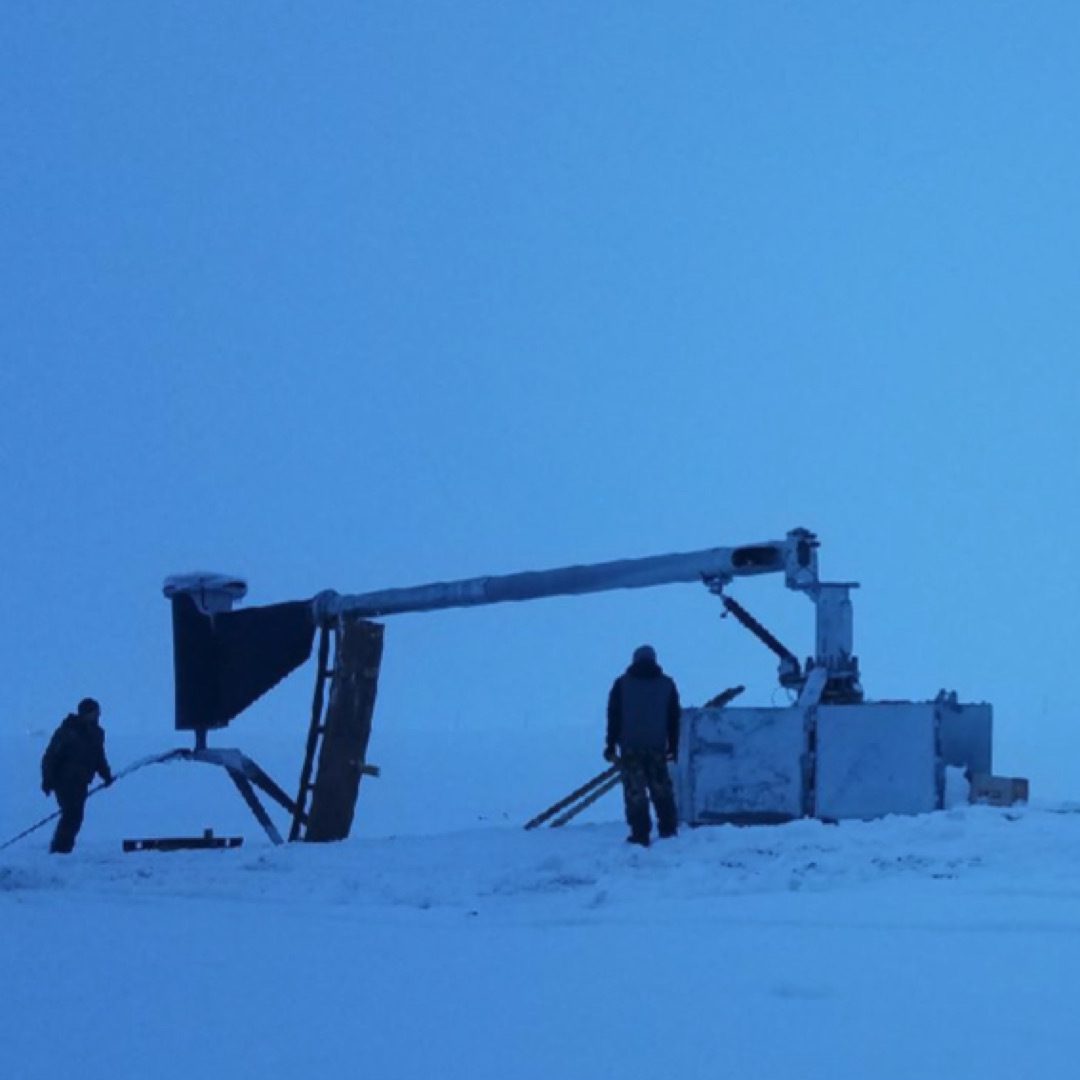
Normally, mid-hinged poles are equipped with 2-4 lights at the top, but they can also support other equipment as required. The adaptability in the design allows for the addition of heavier or more complex setups, such as wind turbines, as demonstrated in the example from the Arctic. This adaptability is crucial for applications in varied environments and for different functionalities.
Mechanisms for Operation
The most common mechanism for operating these poles is a winch system, which can be either hand-operated or motorized:
- Hand Winch: Preferred by about 95% of customers, the hand winch is a simple, reliable, and cost-effective solution. It suits most situations where the pole does not carry excessive weight and is not frequently adjusted.
- Motorized Winch: Chosen for ease of use and efficiency, especially when the pole carries heavier loads or is adjusted more frequently. A motorized winch with a steel cable provides durability and strength.
- Counterweights: These are used to balance the weight of the pole and mounted equipment, facilitating easier and safer operation. The inclusion of counterweights helps manage the physical effort required to raise and lower the pole, particularly with heavier loads.
Installation and Base Structure
Mid-hinged poles often use a quick base system, which allows for rapid installation without the need for extensive ground preparation or massive concrete bases. This feature is particularly beneficial in challenging environments, such as the Arctic, where traditional installation methods may be impractical. The quick base sits directly on the ground and provides stable support, simplifying the installation process and reducing overall costs.
Speed Control
The operator can control the speed of raising and lowering the pole. This control is crucial for ensuring the safety of both the equipment and the operator, particularly in adverse weather conditions or when handling sensitive or heavy equipment.
Flexibility and Adaptability
The flexibility in design and operation makes mid-hinged poles a suitable choice for a variety of locations and applications, from urban settings requiring frequent maintenance to remote areas like the Arctic, where robust and adaptable infrastructure is necessary.
As the photo on the left demonstrates, just about anything is possible. The photo is of a wind turbine mounted on a mid hinged pole with counterweights and a winch. The structure on the bottom is a quick base that sits on the ground. It does not require a massive concrete base for installation. The location is the artic.
Do you have questions? Contact us today.
Mid Hinged Light Poles: Structure and Engineering
The engineering and construction of mid-hinged light poles, such as those provided by Access Fixtures, are meticulously tailored to meet specific functional requirements across various applications. This customization allows them to support multiple uses, from basic lighting to complex setups involving wind energy generation and solar panels. The list below highlights engineering and galvanized steel specifications.
Engineering Standards and Compliance
- ANSI/TIA-222-G (DS1-2011): This U.S. standard is primarily for the design of telecom and wind turbine towers. It ensures that structures are capable of withstanding environmental loads such as wind and seismic activities, which is crucial for the stability of mid-hinged poles, especially in exposed locations.
- IEC 61400-1-2 2006: This is an international standard that specifies requirements for wind turbine design and support structures. It’s particularly relevant for mid-hinged poles used in wind energy applications, ensuring they are engineered to support the dynamic loads imposed by wind turbines.
- EN 1090-1-2008, -2-2009: These European standards cover the technical requirements for the execution of steel structures. Compliance ensures that the welding and structural integrity meet high safety and quality standards, which is essential for the long-term durability of mid-hinged poles.
- Eurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures Part 1-9: Fatigue: This part of Eurocode 3 deals specifically with fatigue analysis of steel structures, an important aspect for mid-hinged poles which may experience numerous stress cycles over their lifetime due to repeated lowering and raising.
- AASHTO 1994 – Version 3 Release Sept. 17th, 2009: This American standard provides guidelines for the design and fatigue life of high-mast structures such as light poles, ensuring they can endure the stresses from environmental factors over many years.
- ASCE 7-2005: This standard sets forth the minimum design loads for buildings and other structures, which includes provisions for wind and seismic loads, contributing to the robustness and safety of the structures.
- ACI 318-08: This code outlines the requirements for structural concrete, which may be used in the foundation designs of mid-hinged poles, ensuring adequate support and stability.
- AWS D1.1: The American Welding Society’s code for structural welding is critical for ensuring that all welding operations on steel mid-hinged poles are performed to the highest standard, providing strength and integrity to the joints.
- CSA W47.1: This Canadian standard for fusion welding of steel is akin to AWS D1.1, and adherence ensures that welding quality meets rigorous safety and durability criteria.
- Standard Specifications for Structural Supports for Highway Signs, Luminaires, and Traffic Signals: These specifications ensure that structures designed to hold signs, lights, and signals are safe, reliable, and capable of withstanding the intended loads.
- AS/NZS 1170.2: This standard provides guidelines for structural design actions for wind actions in Australia and New Zealand, ensuring that structures like mid-hinged poles are capable of withstanding local wind conditions.
Customization and Application
Access Fixtures focuses on designing and manufacturing mid-hinged poles that meet the diverse needs of their clients, whether it’s integrating lighting with wind turbines or customizing the pole to fit specific environmental conditions like those in the Arctic. Using galvanized steel in the poles ensures durability and resistance to harsh weather conditions, making these poles suitable for a wide range of geographical locations and applications.
By adhering to these standards, mid-hinged light poles are guaranteed to be reliable, safe, and effective, tailored to meet the specific demands of any site or project. This rigorous approach to design and engineering enhances functionality and extends the lifespan and reduces the maintenance needs of these versatile structures.
Comparing Mid-Hinged Light Poles with Base-Hinged Light Poles
When considering the implementation of hinged light poles, it’s important to understand the functional distinctions between mid-hinged and base-hinged models. These differences significantly impact their performance, ease of operation, and potential applications.
Mid-Hinged Light Poles
- Structure and Operation: Mid-hinged light poles feature a hinge point located around the middle of the pole. This design allows the pole to bend from the midpoint, making it more accessible when maintenance or adjustment is needed. The leverage provided by the hinge’s placement facilitates easier and safer operations.
- Ease of Use: One of the key advantages of mid-hinged poles is their ease of operation. They can typically be raised and lowered by a single person using a manual or motorized winch system. This operation does not require specialized heavy machinery, making it less costly and logistically simpler.
- Time Efficiency: Raising and lowering a mid-hinged pole takes about a minute, making it extremely efficient for tasks requiring frequent access to mounted equipment, such as lighting adjustments or repairs.
Base-Hinged Light Poles
- Structure and Operation: In contrast, base-hinged poles have their hinge mechanism at the very bottom, near the base. This design means the entire length of the pole must be lifted vertically, which can be considerably more challenging due to the lack of mechanical advantage that mid-hinged poles benefit from.
- Equipment Requirements: Raising and lowering base-hinged poles typically requires mechanical aids such as a lull or crane. This requirement is due to the direct lift needed to move the pole, as there is no internal mechanism similar to the winch system in mid-hinged poles that aids the lifting process.
- Operational Complexity: Because base-hinged poles rely on external equipment for movement, the process is generally more labor-intensive and costly. It also requires more space for the equipment to operate and may not be suitable in tightly confined areas.
Comparative Analysis
- Flexibility and Convenience: Mid-hinged poles offer greater flexibility and convenience, particularly in environments where rapid and frequent access to the pole top is necessary. Their design minimizes the need for additional equipment and manpower.
- Safety and Risk: Mid-hinged poles also tend to be safer to operate since they require less manual interaction during the raising and lowering process, reducing the risk associated with handling long, heavy objects.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Operating base-hinged poles often involves higher costs due to the need for heavy lifting equipment and potentially more personnel. In contrast, mid-hinged poles can be more cost-effective due to their simpler, less resource-intensive operation.
Therefore, the choice between mid-hinged and base-hinged light poles will depend on the specific needs of the project, including considerations of safety, cost, and operational efficiency. Mid-hinged poles generally offer more user-friendly features for locations requiring frequent maintenance or adjustments, while base-hinged poles may be suitable for installations where the pole is not frequently adjusted.
Get an Overview of Light Poles for LED Lighting.
Learn about High-Mast Light Poles.
Conclusion
Mid-hinged light poles represent a significant advancement in pole technology, offering substantial benefits over traditional and base-hinged models, particularly in terms of maintenance, safety, and operational efficiency. Their design addresses the practical challenges of servicing high installations while also catering to aesthetic considerations in scenic areas. By adhering to rigorous engineering standards, these poles ensure reliability, durability, and compliance with both national and international safety codes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary benefits of mid-hinged light poles compared to traditional poles? Mid-hinged poles offer easier access for maintenance, enhanced safety by eliminating the need to climb, quicker adjustment times, and less visual intrusion in scenic areas.
Can mid-hinged poles support heavy equipment like wind turbines? Yes, mid-hinged poles can be custom-engineered to support additional loads such as wind turbines and solar panels, depending on the specific design and structural calculations to ensure stability and safety.
Are there any limitations on the height of mid-hinged light poles? While there is no strict limit to the height, mid-hinged light poles are typically designed to stand up to 65 feet. The exact height and capacity can be tailored to meet specific site requirements and environmental conditions.
What types of winch systems are available for operating mid-hinged poles? Mid-hinged poles can be equipped with either hand winches or motorized winches. The choice depends on the specific needs, such as the weight of the pole and the frequency of adjustments.
How are mid-hinged poles installed in difficult environments like the Arctic? These poles often use a quick base system that allows for easy and rapid installation without the need for massive concrete bases, making them suitable for challenging environments where traditional installation methods are impractical.